- 3% Discount on online orders
- Fast Delivery Times
- DIN ISO 9001:2015 Certified
- Manufacturer Expertise
- Contact Us
Checkout using your account
Checkout as a new customer
Creating an account has many benefits:
- See order and shipping status
- Track order history
- Check out faster
Reversed Phase Chromatography
Reversed Phase Chromatography (RP) is the most commonly used method of liquid chromatography. It is characterised by stationary phases with non-polar surface properties and a mobile phase of polar character - exactly the opposite of normal phase chromatography.
You will find an introduction to the basics of reversed-phase chromatography on this page as well as an overview of HPLC columns suitable for this separation technique.
We will be happy to help you select the right column for your analytical problem.
Products
Technical Data
Basics
Stationary phases of reversed-phase chromatography
Surface-modified (C30, C18, C8, C4,C1, C6H5,...) silica gels are often used as stationary phases. These can be produced comparatively easily and in large quantities and have high mechanical and chemical stability as well as reproducibility.
Other materials used as stationary phases in reversed phase chromatography are
- Hydrophobic polymers, e.g. styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer (PS-DVB)
- Modified hydrophilic polymers, e.g. C18-modified polyvinyl alcohol
- Graphitised carbon, e.g. Hypercarb™
- Modified metal oxide particles, e.g. zirconium oxide particles coated with carbon
Surface modification of silica gel
When modifying silica gel, the silanols present on the surface (free Si-OH groups) are chemically reacted with non-polar groups. This process inevitably always leaves free residual silanols, as it is not possible to get all silanols to react due to steric reasons. These residual silanols sometimes lead to unwanted interactions between analyte and stationary phase, which - if conditions are not adapted - can result in insufficient separation performance, adsorption or peaktailing.
In addition to free silanols, impurities in the base silica gel, e.g. metal ions, can also lead to undesirable polar interactions. For this reason, almost all stationary phases today are based on high-purity silica gel ("Type B silica").
The simplest approach to minimise the proportion of residual silanols is so-called end-capping. The remaining residual silanols are reacted with small alkylating reagents, such as trimethylsilyl (TMS) groups. In addition to conventional endcapping, other methods are also used to shield residual silanols. The aim is always to ensure that the analytes do not come into contact with free silanols.
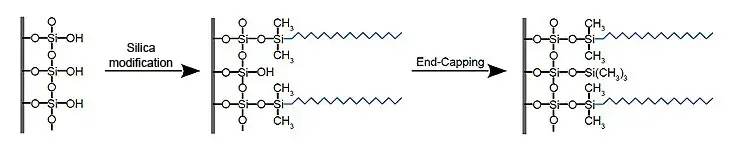
Figure 1: Schematic representation of silica modification and subsequent end capping.
The separation mechanism of reversed-phase chromatography
In classical reversed-phase chromatography, the separation mechanism is mainly based on the different distribution of analytes between the stationary and mobile phases. This phenomenon can also be understood as a kind of extraction of the analytes between the stationary and mobile phases. This means that a non-polar analyte dissolves preferentially in the stationary phase, remains there and is thus eluted slowly from the column. Polar compounds, on the other hand, are rinsed from the column very quickly, as they prefer to remain in the mobile phase.
With negligibly small proportions of free residual silanols, only hydrophobic interactions (van der Waals forces) contribute to the separation. Depending on the silica modification, other interactions can also contribute to the separation, e.g. π-π interactions in phenyl-modified stationary phases or weak ion exchange interactions in the presence of free silanols.
Mobile phases of reversed-phase chromatography
The mobile phase used in reversed-phase chromatography almost always contains water as the component with the lowest elution power and a water-miscible solvent, which increases the elution power of the mobile phase. Methanol, acetonitrile or tetrahydrofuran are usually used for this purpose, which differ from each other not only in their elution power, but also in the selectivity of the interactions they have with the analytes and the stationary phase.
How do I choose the right reversed phase column?
Reversed phase chromatography is by far the most widely used separation technique. Therefore, every manufacturer has a variety of different modifications and base materials for the reversed phase. The influence of pore size and other physical properties can be found on our page HPLC columns page.
Due to the large number of different phases, choosing the right column is not easy and also depends on the analytes. The easiest way is to do a literature search or to look at manufacturers or in the Pharmakopoeia. We are happy to support you in this. Please contact us!
However, there are a few considerations to narrow down the choice:
- basic compounds: a high pH value (> 8) of the mobile phase could be favourable → column with high pH stability or polymer
- Acidic compounds: a low pH value (< 1) of the mobile phase could be favourable → column with high pH stability
- very polar compounds: 100% water in mobile phase may be necessary or polar interaction → column for 100% water, polar modified column (polar embedded, polar endcapped)
- very hydrophobic compounds: retention may be too long → column with lower carbon loading, more organics in the mobile phase
Other parameters can also influence the separation. These include, for example, the choice of ligand. This can be a C2 to C30 group, fluorinated phases, phenyl groups, cyano groups, polar modified phases or encapsulated phases (with a polymer on the silica surface). Each phase offers different interactions to influence the selectivity of the separation.
- C18 chain: most commonly used phase, shows good retention for a variety of analytes is usually used as the first phase
- C8 chain: same interactions as C18 but shorter retention
- C4 chain: less polar than C8 and more polar interaction, often for proteins and peptides
- Phenyl: non-polar and possibility for π-π interactions, special selectivity for aromatics
- Cyano: quite polar, interaction with free electron pairs, alternative selectivity to C18
- Fluorinated phases: polar and aromatic (PFP), selectivity for halogenated and polar aromatic compounds
- polar modified phases: polar and non-polar interactions, better peak shape for acidic and basic analytes, can be used with 100% water
Manufacturers and columns for reversed-phase chromatography
Almost all manufacturers or suppliers of HPLC columns now have several reversed-phase columns in their range. The variety of available phases and selectivities is enormous. We are happy to support you in finding and selecting a suitable column for your analysis. Below you will find a small selection of reversed phase HPLC columns that are frequently used.
The right column for you - we will be happy to support you individually
Competent consultants are always at your side. Write a message to our consultants, we will get back to you and give you individual support.
You will find:
Write us a message and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
